Abstract
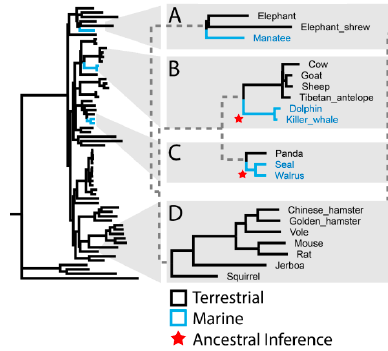
The quest to map the genetic foundations of phenotypes has been empowered by the modern diversity, quality, and availability of genomic resources. Despite these expanding resources, the abundance of variation within lineages makes it challenging to associate genetic change to specific phenotypes, without an a priori means of isolating the changes from background genomic variation. Evolution provides this means through convergence—i.e., the shared variation that may result from replicate evolutionary experiments across independent trait occurrences. To leverage these opportunities, we developed TRACCER: Topologically Ranked Analysis of Convergence via Comparative Evolutionary Rates. Compared to current methods, this software empowers rate convergence analysis by factoring in topological relationships, because genetic variation between phylogenetically proximate trait changes is more likely to be facilitating the trait. Comparisons are performed not with singular branches, but with the complete paths to the most recent common ancestor for each pair of lineages. This ensures that comparisons represent a single context diverging over the same timeframe while obviating the problematic requirement of assigning ancestral states. We applied TRACCER to two case studies: mammalian transitions to marine environments, an unambiguous collection of traits which have independently evolved three times; and the evolution of mammalian longevity, a less delineated trait but with more instances to compare. By factoring in topology, TRACCER identifies highly significant, convergent genetic signals, with important incongruities and statistical resolution when compared to existing approaches. These improvements in sensitivity and specificity of convergence analysis generates refined targets for downstream validation and identification of genotype-phenotype relationships.